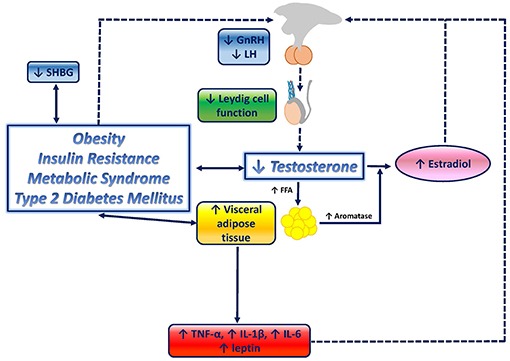
SHBG, or sex hormone-binding globulin, is a protein produced by the liver. Its main function is to
bind to certain hormones in your bloodstream, particularly sex hormones like testosterone and
estrogen. When these hormones are bound to SHBG, they become inactive and unable to exert their
effects on the body’s tissues.
Now, let’s talk about how SHBG levels can affect your hormones. If you have high levels of SHBG, it
means more of your testosterone and estrogen are bound up and less is available for use by your
body’s tissues. This can lead to symptoms of hormone imbalance such as:
- Low libido: Since less testosterone is available to exert its effects, you may experience a
decrease in sex drive. - Fatigue: Testosterone plays a role in energy levels, so low levels of free testosterone due to
high SHBG can contribute to feelings of tiredness and fatigue. - Difficulty building muscle mass: Testosterone is important for muscle growth and repair.
When it’s bound to SHBG and inactive, it can be harder to build and maintain muscle mass. - Mood changes: Hormonal imbalances can affect mood regulation, potentially leading to
mood swings, irritability, or even depression. - Menstrual irregularities: In women, high SHBG levels can affect estrogen levels, potentially
leading to irregular menstrual cycles. - Symptoms of Menopause: In women, elevated SHBG takes up all of the estrogens and
may lead to hot flashes, poor sleep, changing skin and hair texture, etc.
On the other hand, if SHBG levels are low, it means more of your hormones are free and available to
exert their effects. While this might sound beneficial, excessively low SHBG levels can also lead to
hormone imbalances and associated symptoms.
It’s important to note that SHBG levels can be influenced by various factors such as age, sex,
medications, and certain medical conditions. If you’re experiencing symptoms of hormonal
imbalance, now is the perfect time to contact us here at Juvenis Medical to evaluate your hormone
levels and determine the appropriate course of action. Treatment options may include lifestyle
changes, medications, or hormone replacement therapy, depending on the underlying cause of the
imbalance.
